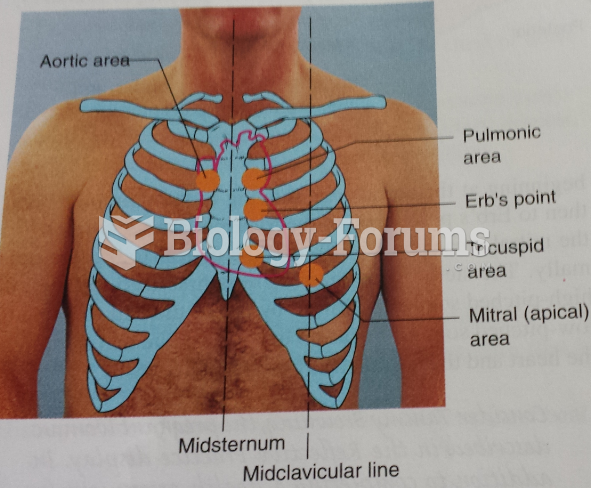
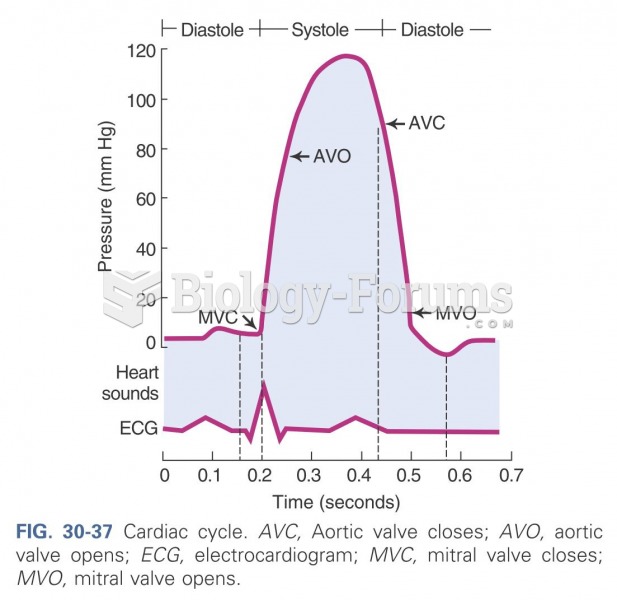
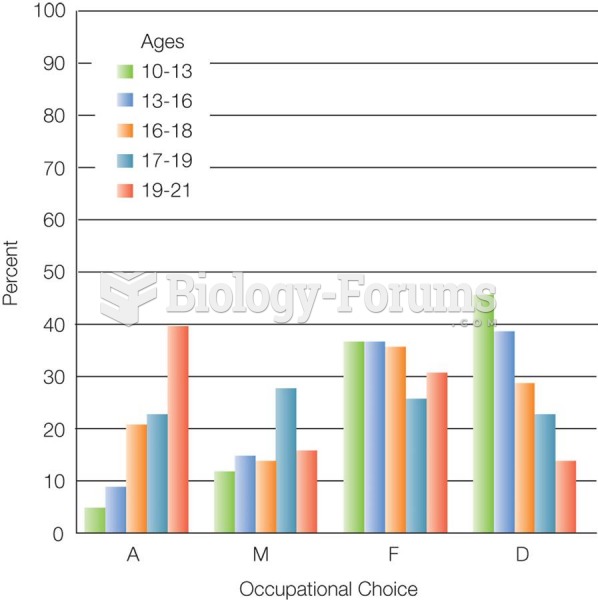
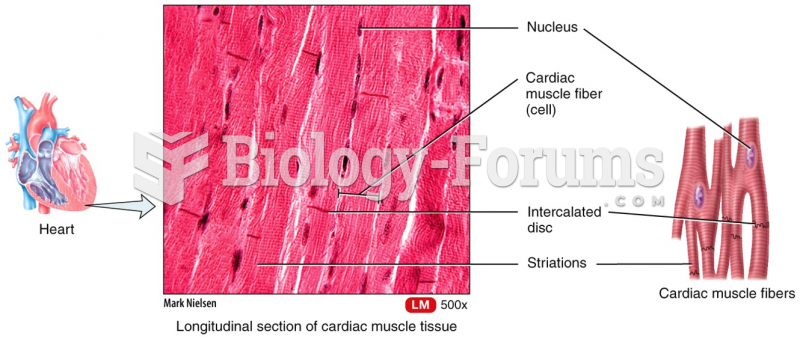
|
|
|
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Lower drug doses for elderly patients should be used first, with titrations of the dose as tolerated to prevent unwanted drug-related pharmacodynamic effects.
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.