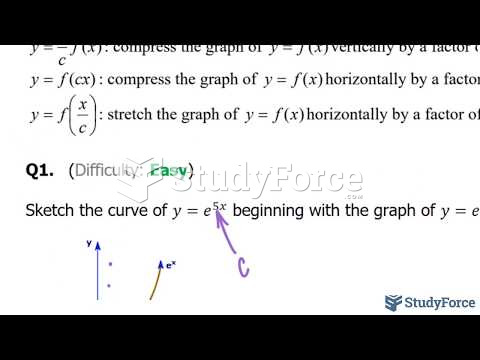
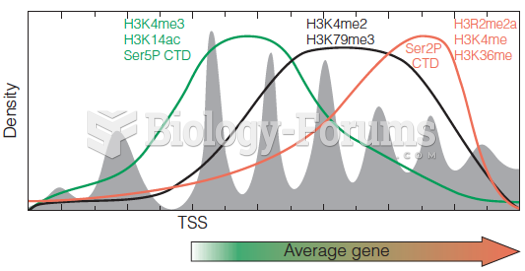
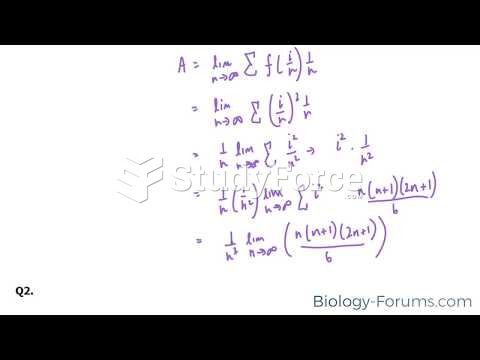|
|
|
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.