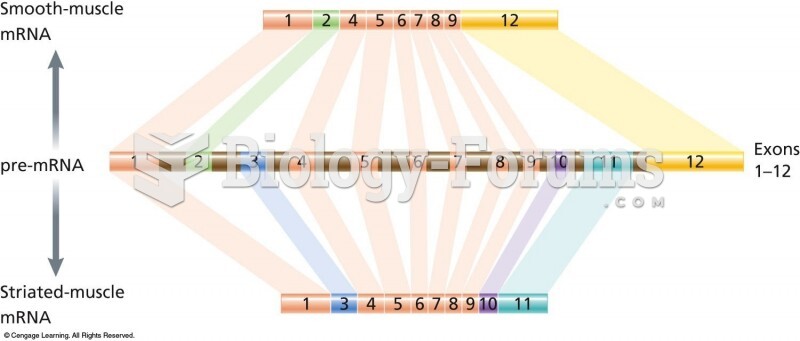
|
|
|
Did you know?
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
Did you know?
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Did you know?
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Did you know?
About 3% of all pregnant women will give birth to twins, which is an increase in rate of nearly 60% since the early 1980s.
Did you know?
Amoebae are the simplest type of protozoans, and are characterized by a feeding and dividing trophozoite stage that moves by temporary extensions called pseudopodia or false feet.