|
|
|
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) was originally known as the Communicable Disease Center, which was formed to fight malaria. It was originally headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, since the Southern states faced the worst threat from malaria.
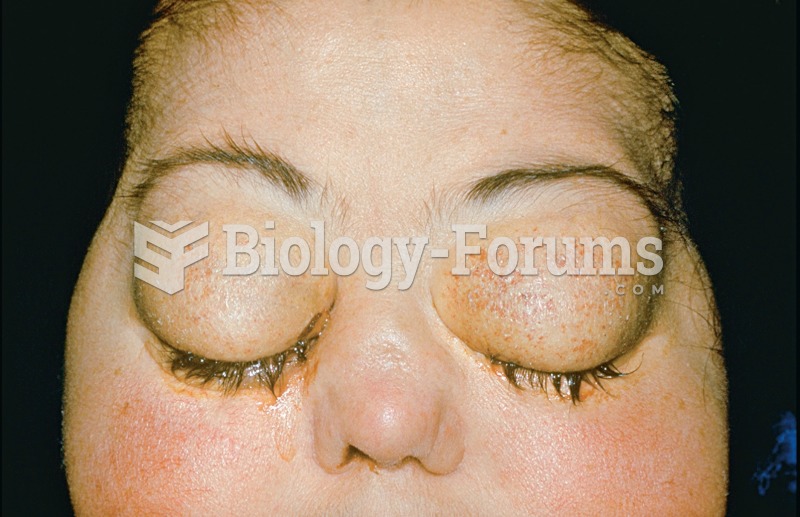
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
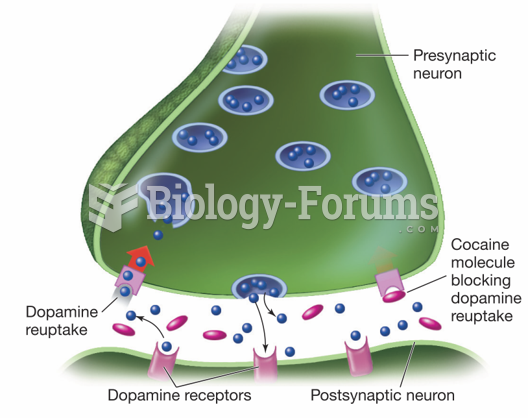
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.