|
|
|
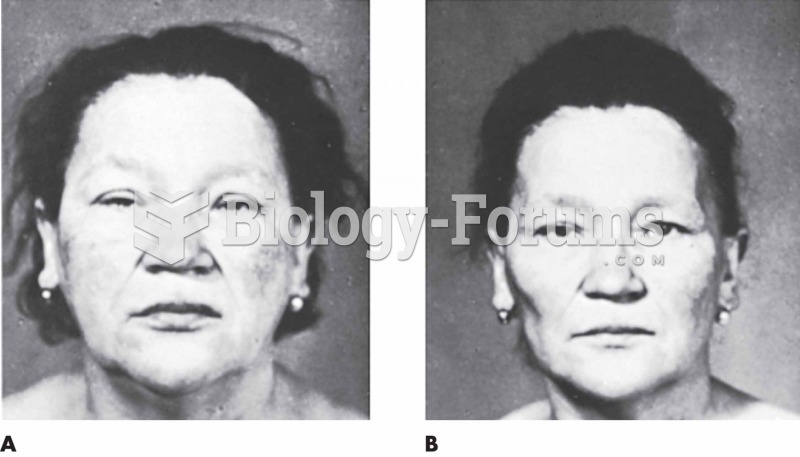
Hippocrates noted that blood separates into four differently colored liquids when removed from the body and examined: a pure red liquid mixed with white liquid material with a yellow-colored froth at the top and a black substance that settles underneath; he named these the four humors (for blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile).
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.