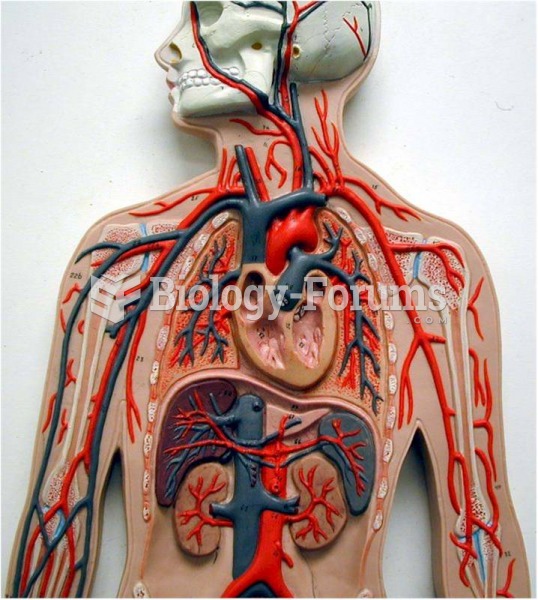
|
|
|
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).
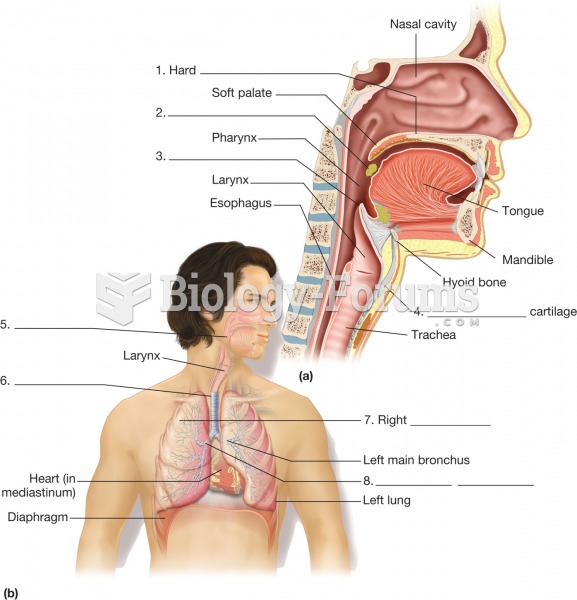 The respiratory system. (a) Sagittal section of the head and neck, revealing the organs of the upper
The respiratory system. (a) Sagittal section of the head and neck, revealing the organs of the upper
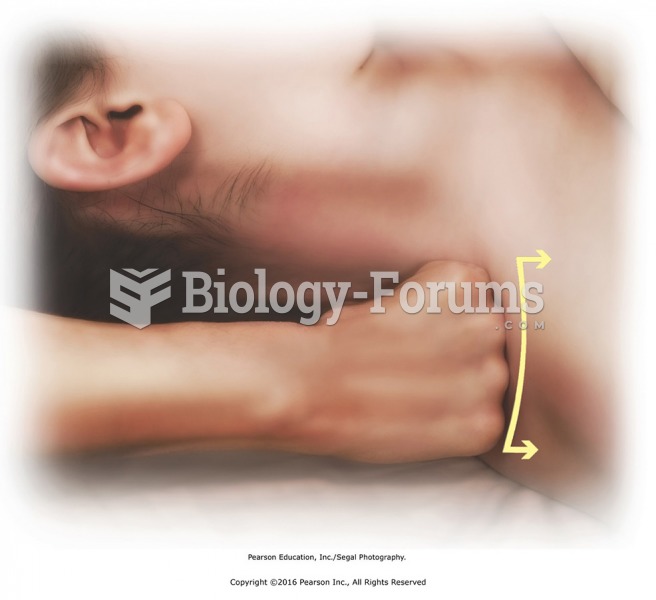 Effleurage along cervical and upper trapezius muscles from occiput to shoulder. Hold head in lateral ...
Effleurage along cervical and upper trapezius muscles from occiput to shoulder. Hold head in lateral ...