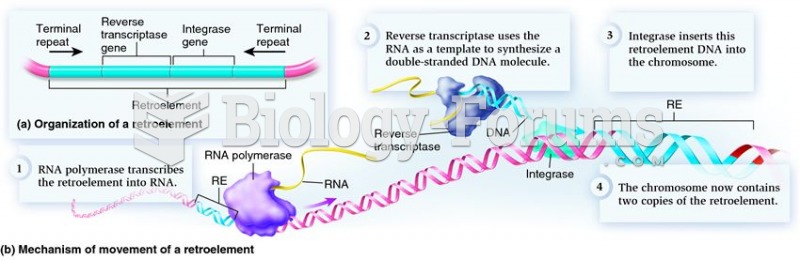
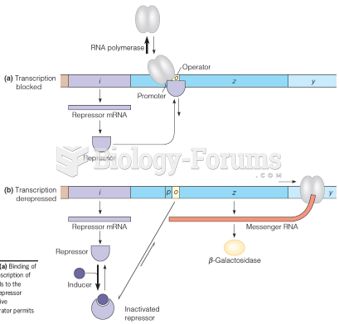
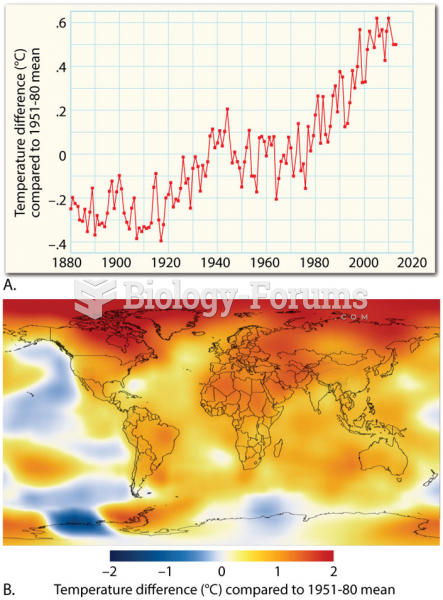
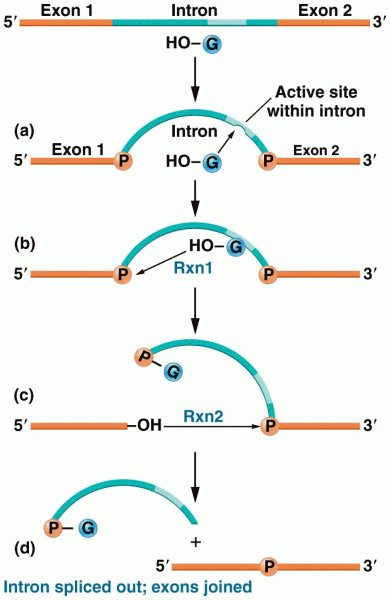
|
|
|
Limit intake of red meat and dairy products made with whole milk. Choose skim milk, low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Limit fried food. Use healthy oils when cooking.
It is believed that the Incas used anesthesia. Evidence supports the theory that shamans chewed cocoa leaves and drilled holes into the heads of patients (letting evil spirits escape), spitting into the wounds they made. The mixture of cocaine, saliva, and resin numbed the site enough to allow hours of drilling.
Urine turns bright yellow if larger than normal amounts of certain substances are consumed; one of these substances is asparagus.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.