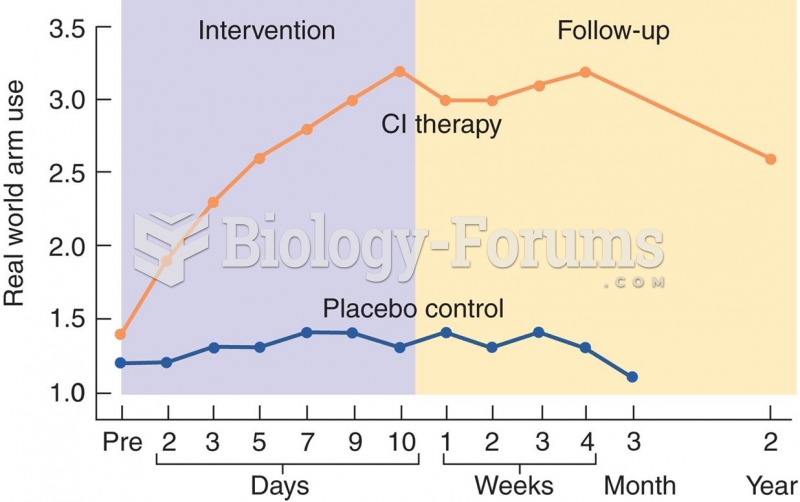
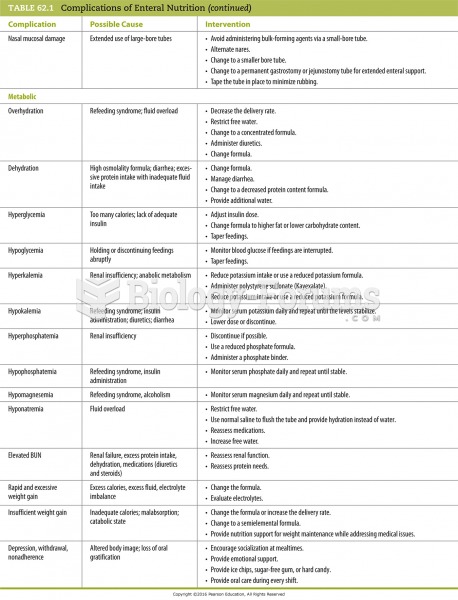
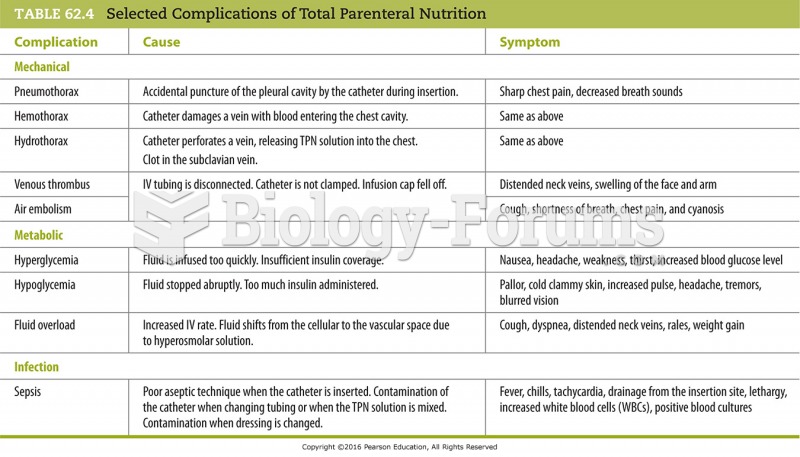
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
Did you know?
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Did you know?
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
Did you know?
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
Did you know?
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.