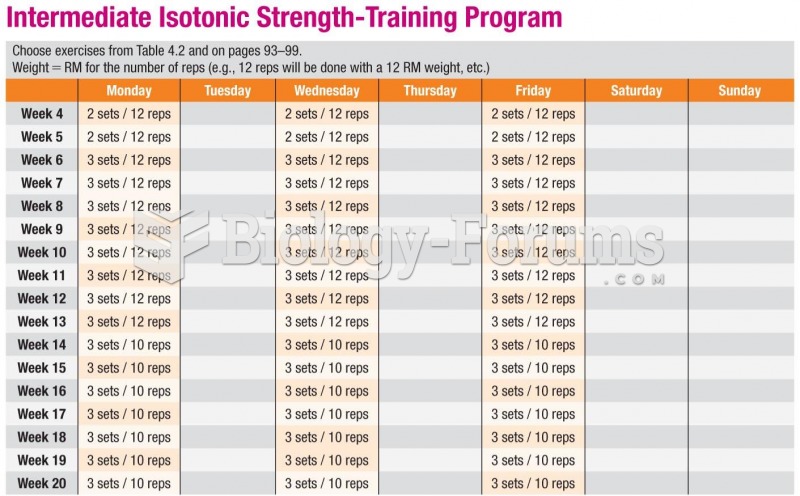
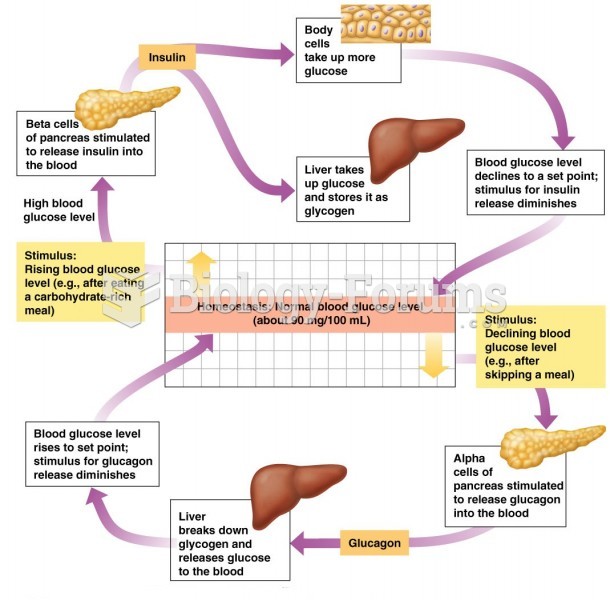
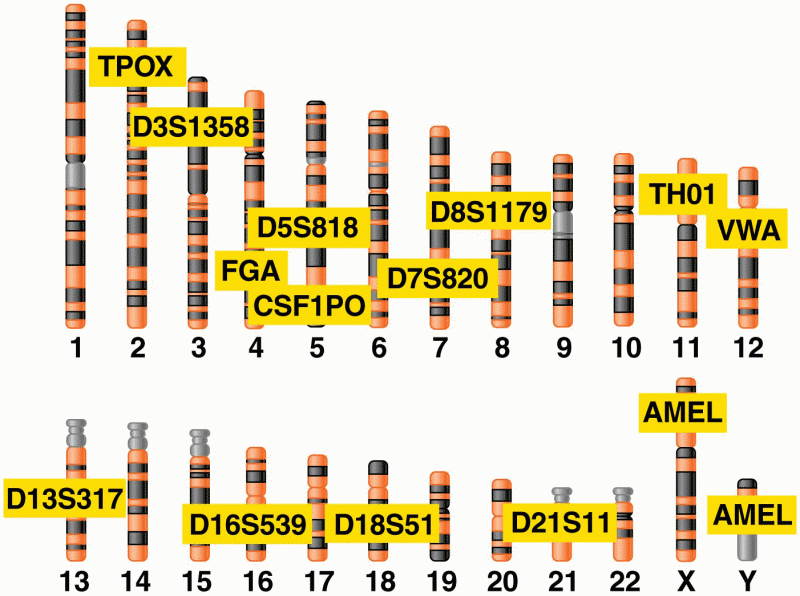
|
|
|
Excessive alcohol use costs the country approximately $235 billion every year.
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.
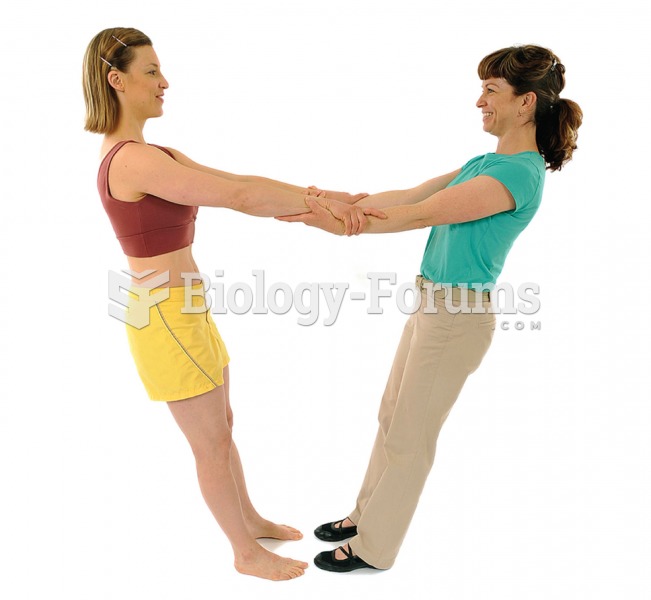
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.