|
|
|
Signs and symptoms that may signify an eye tumor include general blurred vision, bulging eye(s), double vision, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye(s), iris defects, limited ability to move the eyelid(s), limited ability to move the eye(s), pain or discomfort in or around the eyes or eyelids, red or pink eyes, white or cloud spots on the eye(s), colored spots on the eyelid(s), swelling around the eyes, swollen eyelid(s), and general vision loss.
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.
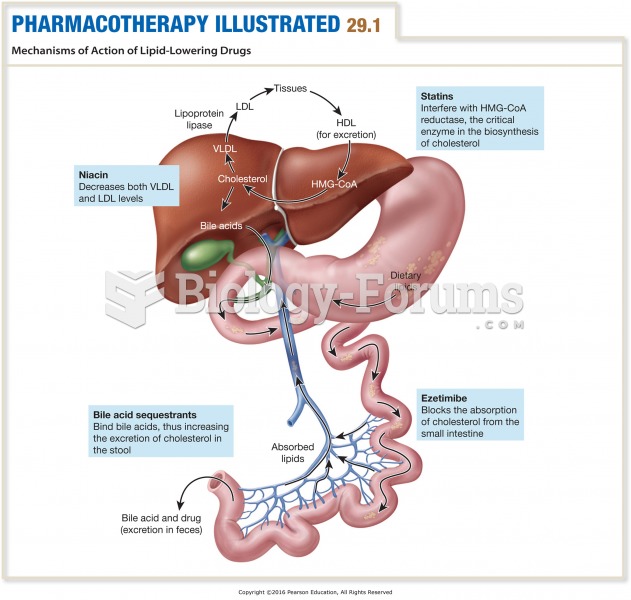
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.