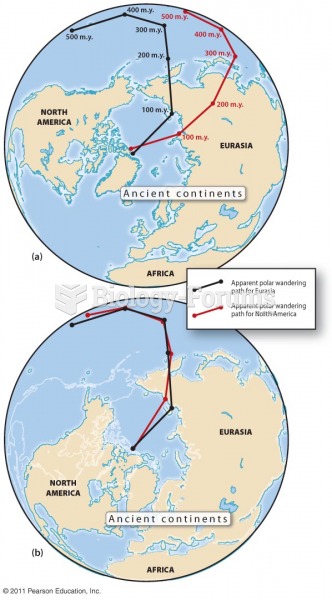
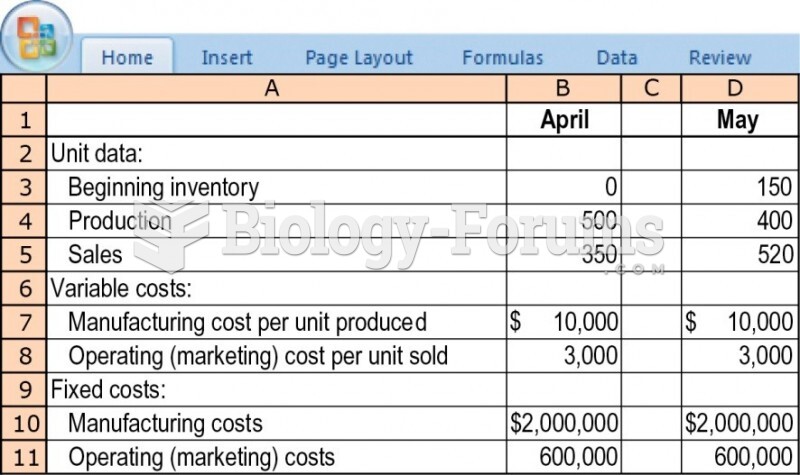
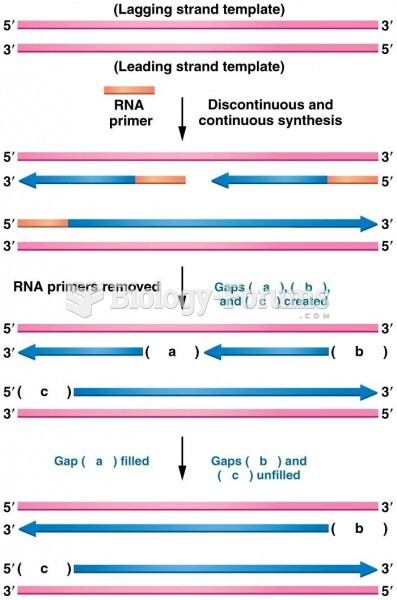
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Did you know?
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
Did you know?
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Did you know?
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Did you know?
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.