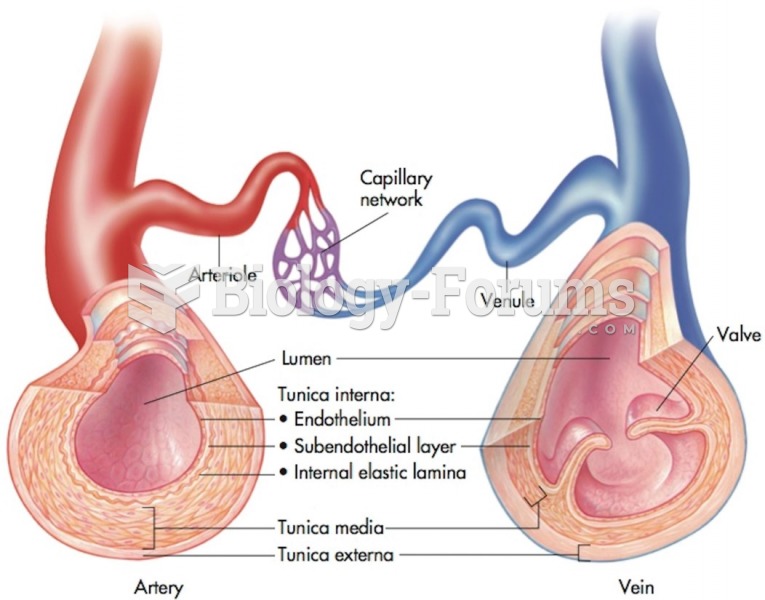
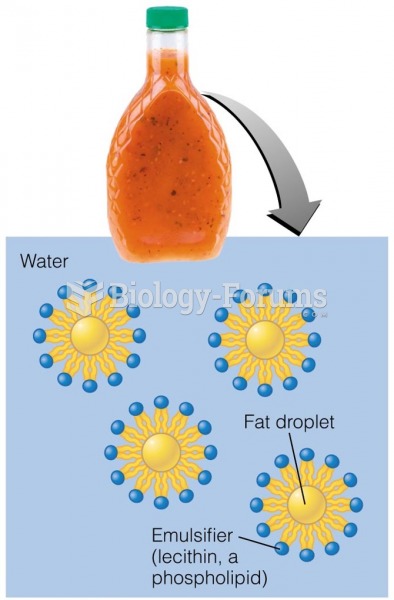
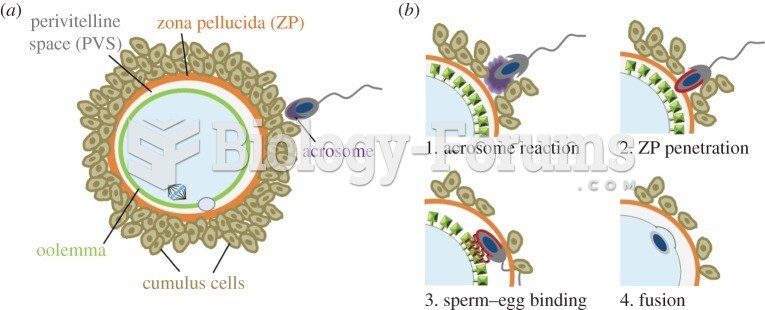
|
|
|
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
Patients who have been on total parenteral nutrition for more than a few days may need to have foods gradually reintroduced to give the digestive tract time to start working again.
Eat fiber! A diet high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by as much as 10%.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).