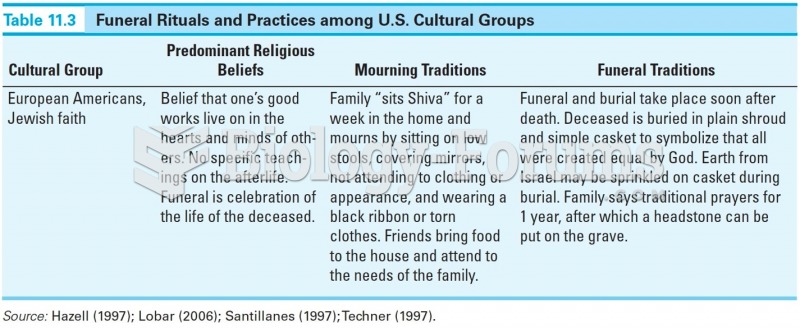
|
|
|
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
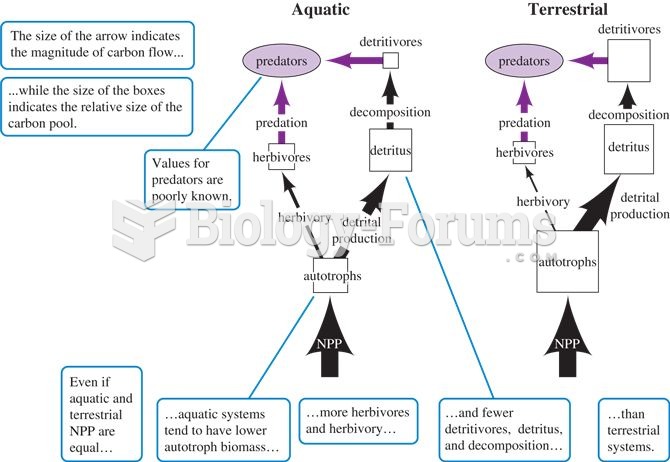 General differences in food webs and carbon flow among terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (adapted f
General differences in food webs and carbon flow among terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (adapted f
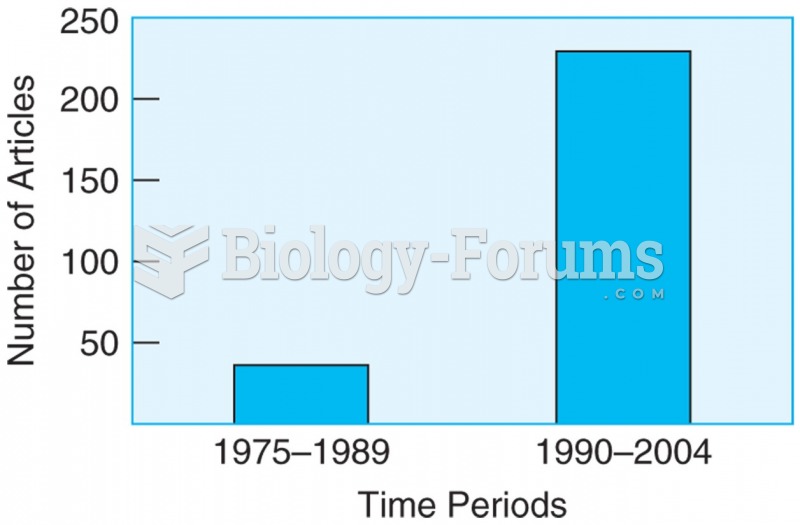 The number of research articles published on the topic of religious practices and spirituality have ...
The number of research articles published on the topic of religious practices and spirituality have ...