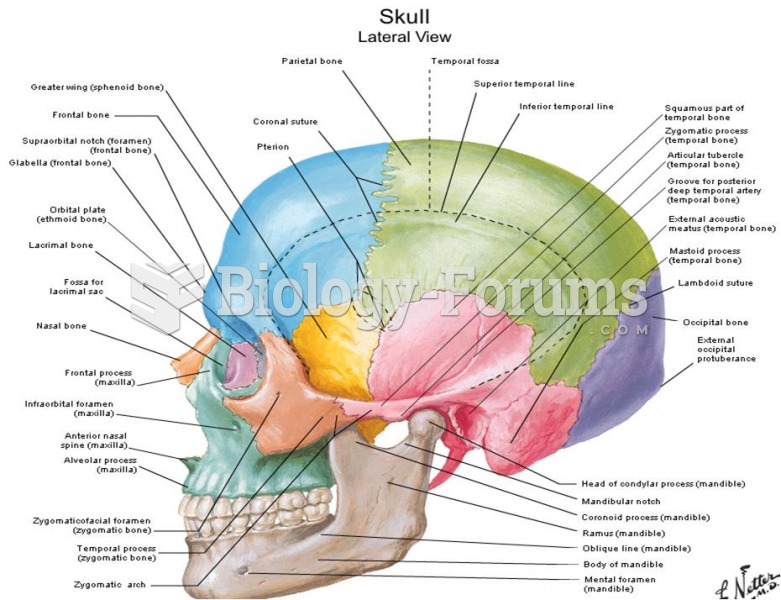
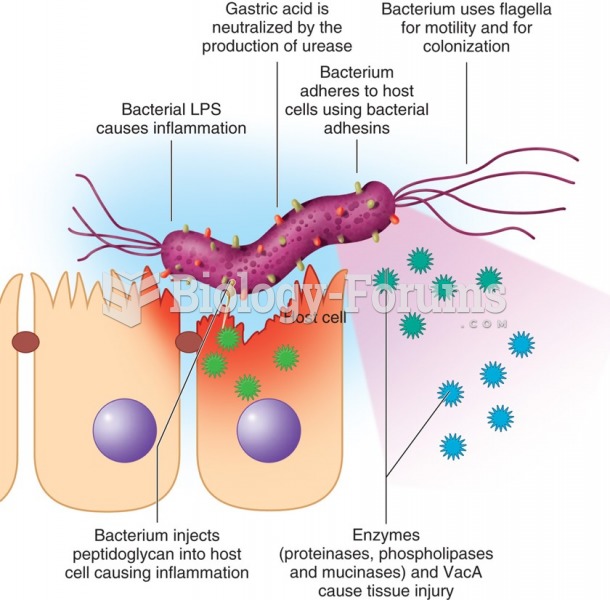
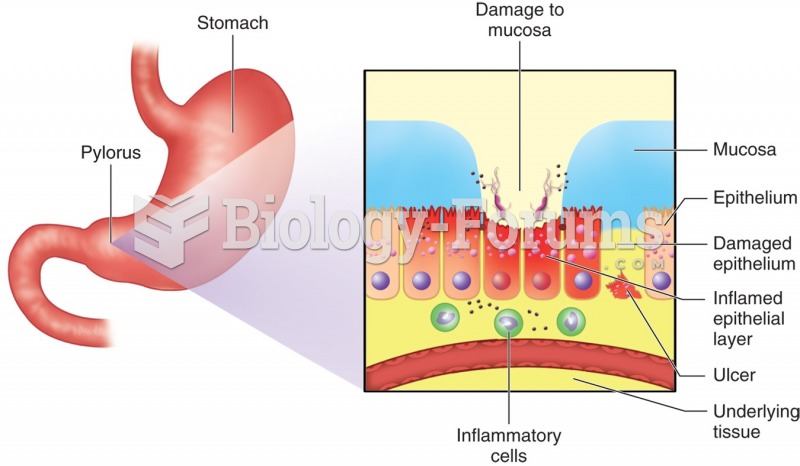
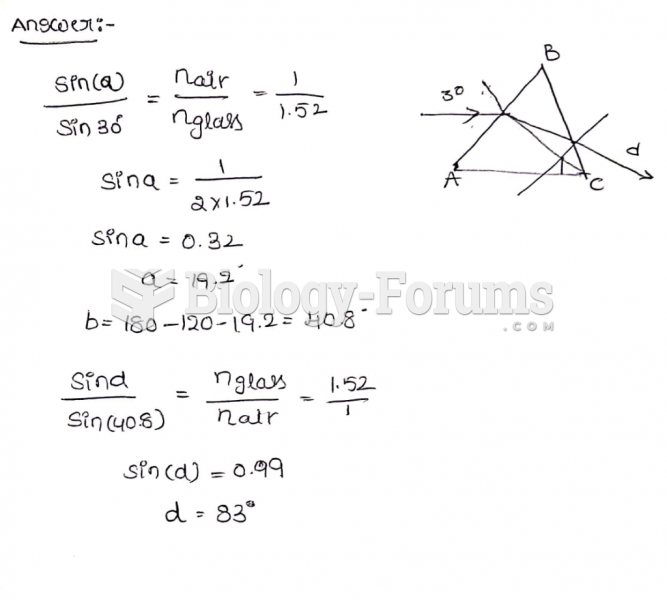
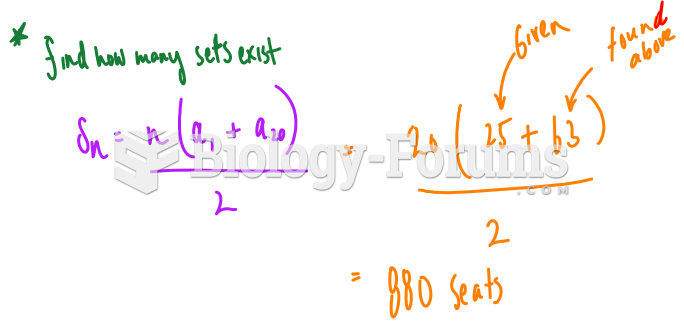|
|
|
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
More than one-third of adult Americans are obese. Diseases that kill the largest number of people annually, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, stroke, and hypertension, can be attributed to diet.
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
In 1886, William Bates reported on the discovery of a substance produced by the adrenal gland that turned out to be epinephrine (adrenaline). In 1904, this drug was first artificially synthesized by Friedrich Stolz.