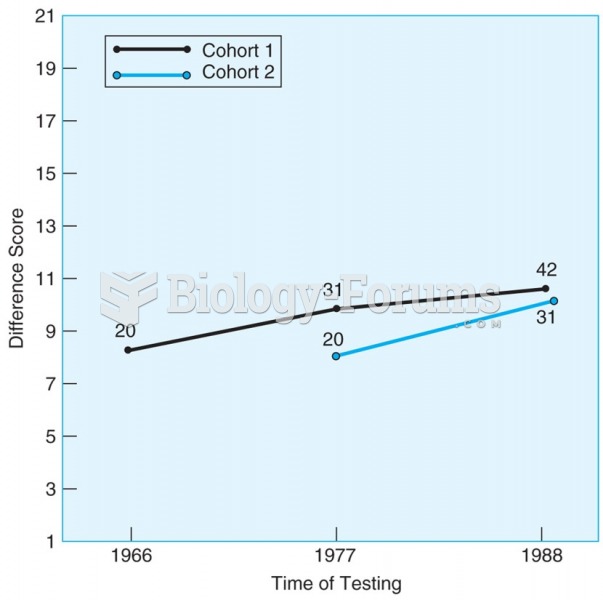
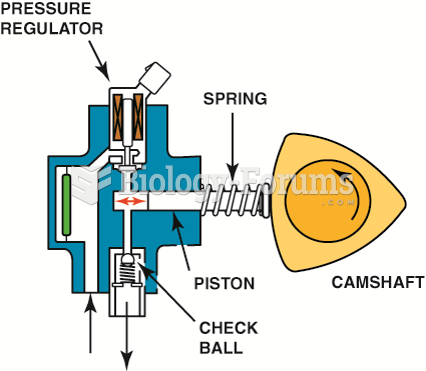
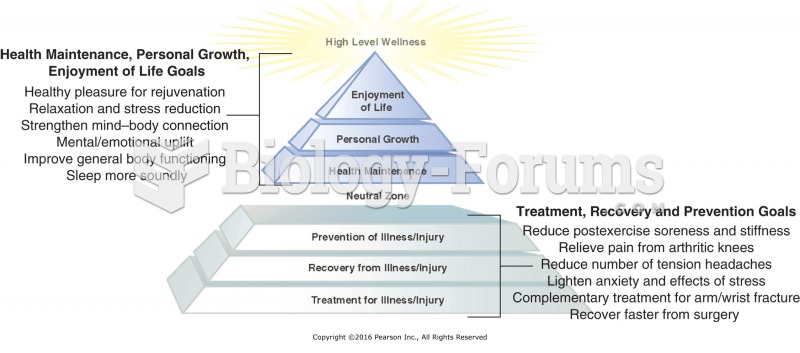
|
|
|
A cataract is a clouding of the eyes' natural lens. As we age, some clouding of the lens may occur. The first sign of a cataract is usually blurry vision. Although glasses and other visual aids may at first help a person with cataracts, surgery may become inevitable. Cataract surgery is very successful in restoring vision, and it is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States.
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.
Opium has influenced much of the world's most popular literature. The following authors were all opium users, of varying degrees: Lewis Carroll, Charles, Dickens, Arthur Conan Doyle, and Oscar Wilde.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.